Photostory by Teresa Rojas
Linking Orangutan Conservation with Forest Peatland Restoration in Central Kalimantan, Indonesia
In 1996, the Government of Indonesia started to implement the Mega Rice Project in Central Kalimantan on the Island of Borneo. The aim was to turn one million hectares of peat swamp forest into rice paddies to contribute to the reduction of Indonesia ́s food shortage. A large investment was made in constructing canals and removing trees. The project failed and was abandoned after making a considerable damage to the environment. Since then, the abandoned area has been subject to severe forest andpeat fires.Borneo Orangutan Survival (BOS), the biggest primate conservation NGO, is working in Kalimantan on the conservation of the Bornean orangutan and its habitat through the involvement of local people. One of the work areas is Mawas. Mawas is a forest conservation, reforestation and research area of 309,000 hectares, located within the ex-Mega Rice Project. Mawas consist of peatlands and it is the home to one of the last tracts of forest supporting wild orangutans. An around 2,800 wild orangutans and many other fauna and flora can be found in this area. Mawas is also important for make it a storage of giga-tonnes of sequestered carbon. BOS in collaboration with other partners and the local communities has been working on restoration of degraded peatlands. The restoration starts with restoring the water table to rewet the surface in order initiate the reforestation, as well as control fire. In order to achieve this, canal blocking strategies are employed. The strategy consists of built dams, which areoverplanted with vegetation. The dammed canals are monitored regularly in order to measure water flow rate and water tables, as well as checking and repairing them. Currently more than 120 canals have been blocked, rewetting about 10000 hectares and 200 hectares of degraded land have been reforested. The photos show the restoration of the peatland forests in Mawas, including the blocking of the channels as well as the efforts to reforest the degraded areas. BOS is convinced that only by involving the localcommunities can we contribute to the restauration of the peatland forests as well as the conservation of biodiversity, including species that are critically endangered such as Orangutans.
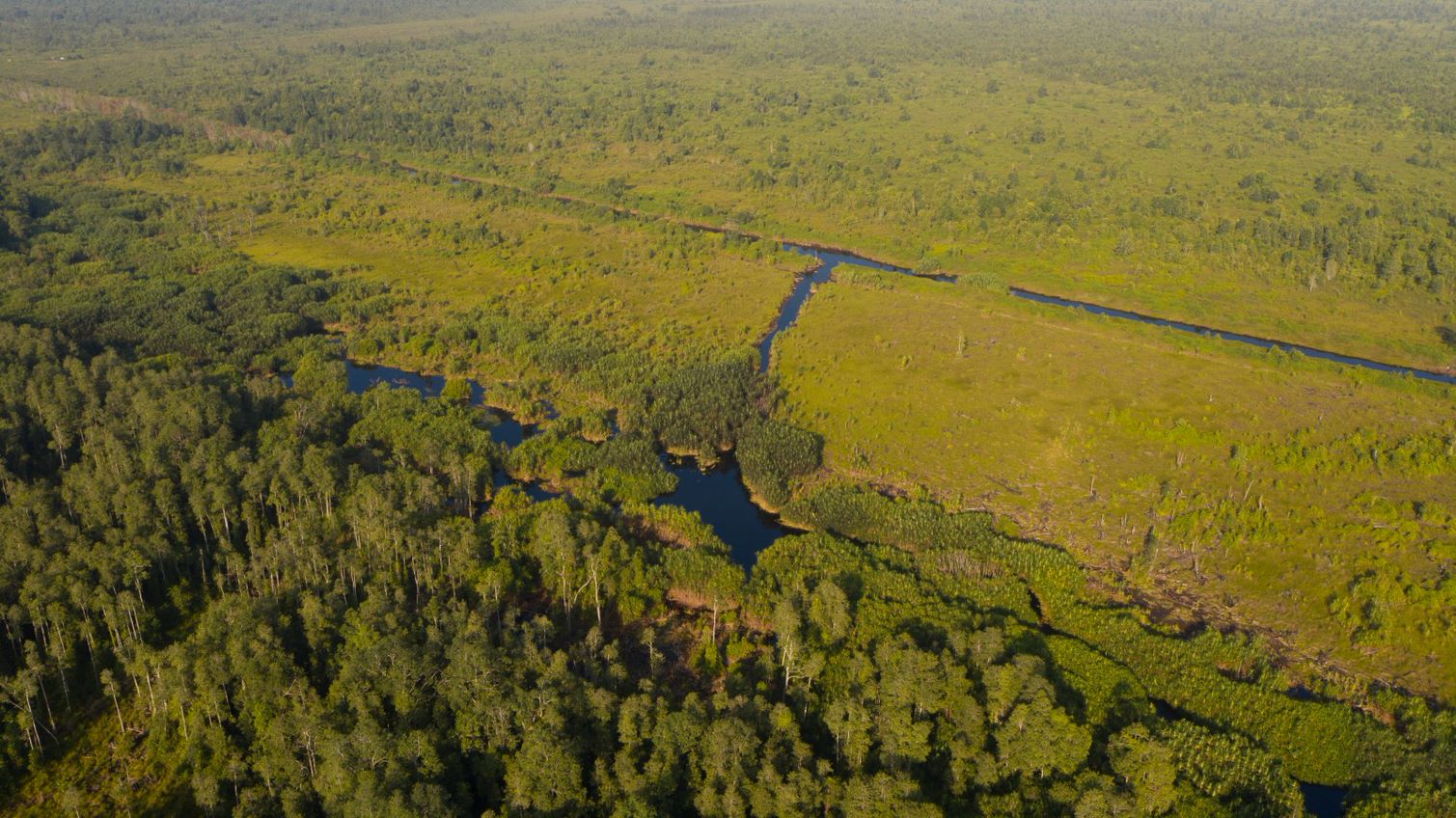

Rehabilitation of peat land forest.
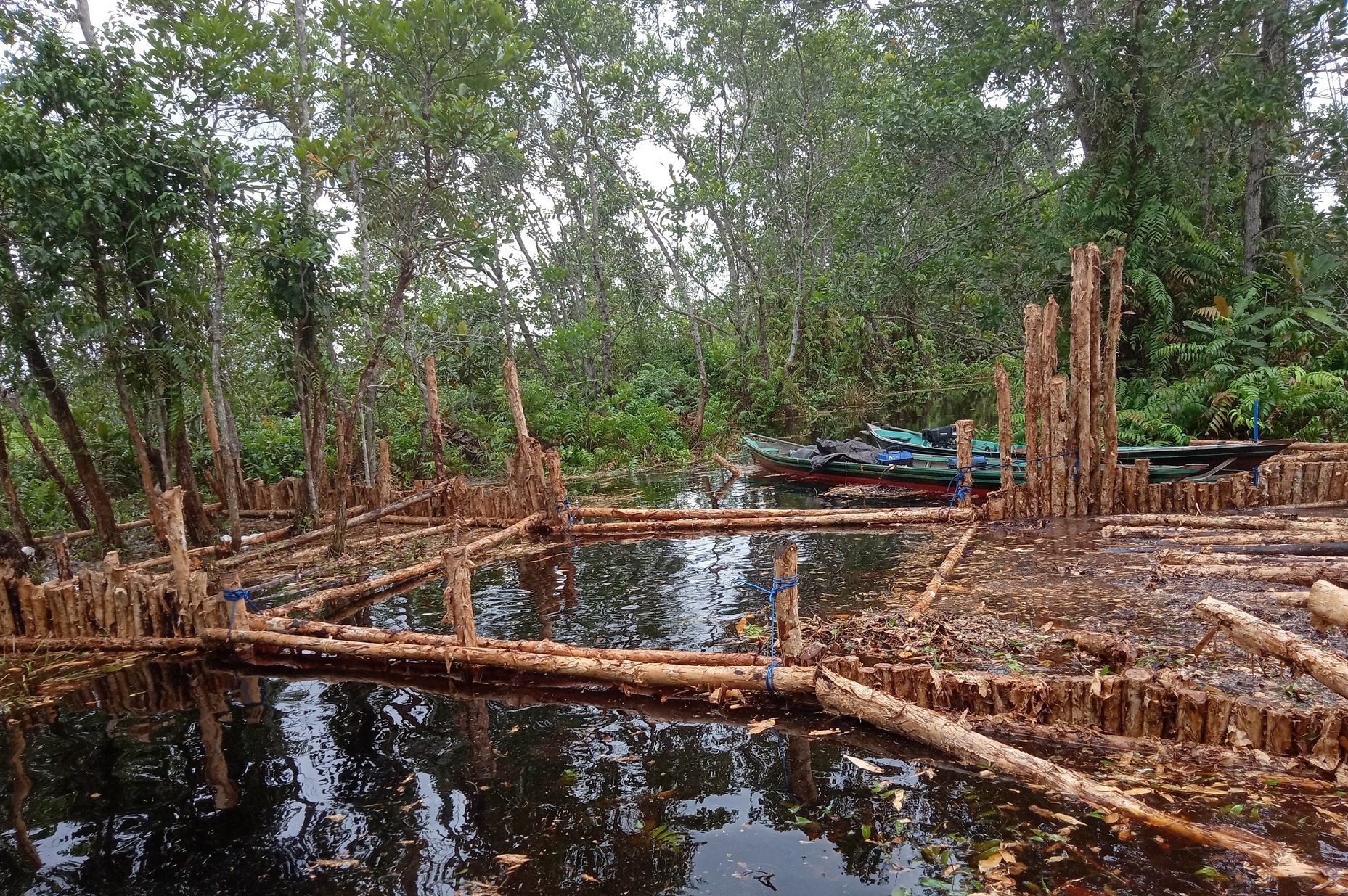

Rehabilitation peat land forest.
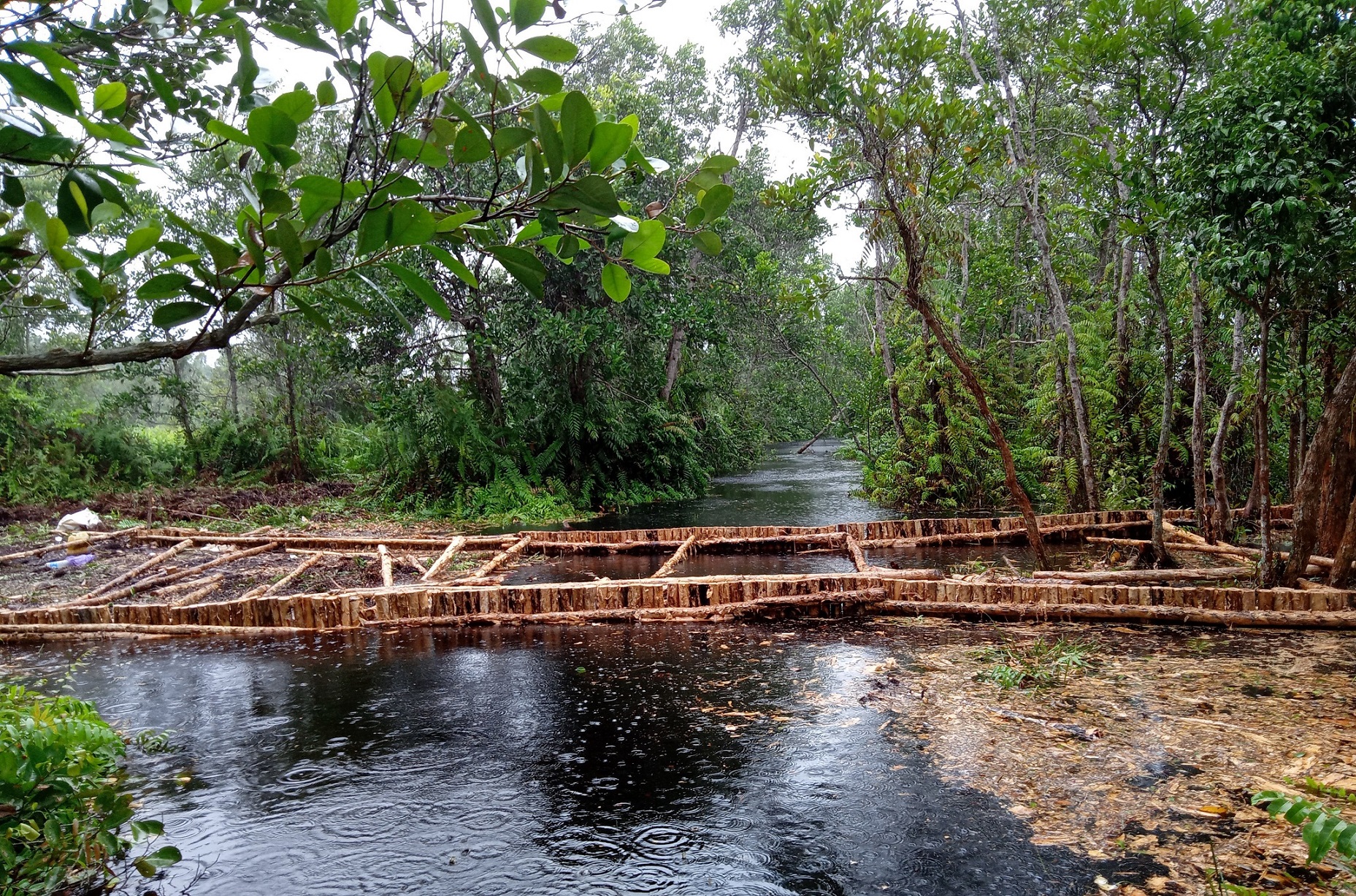

Rehabliitation of peat land forest: Dam.
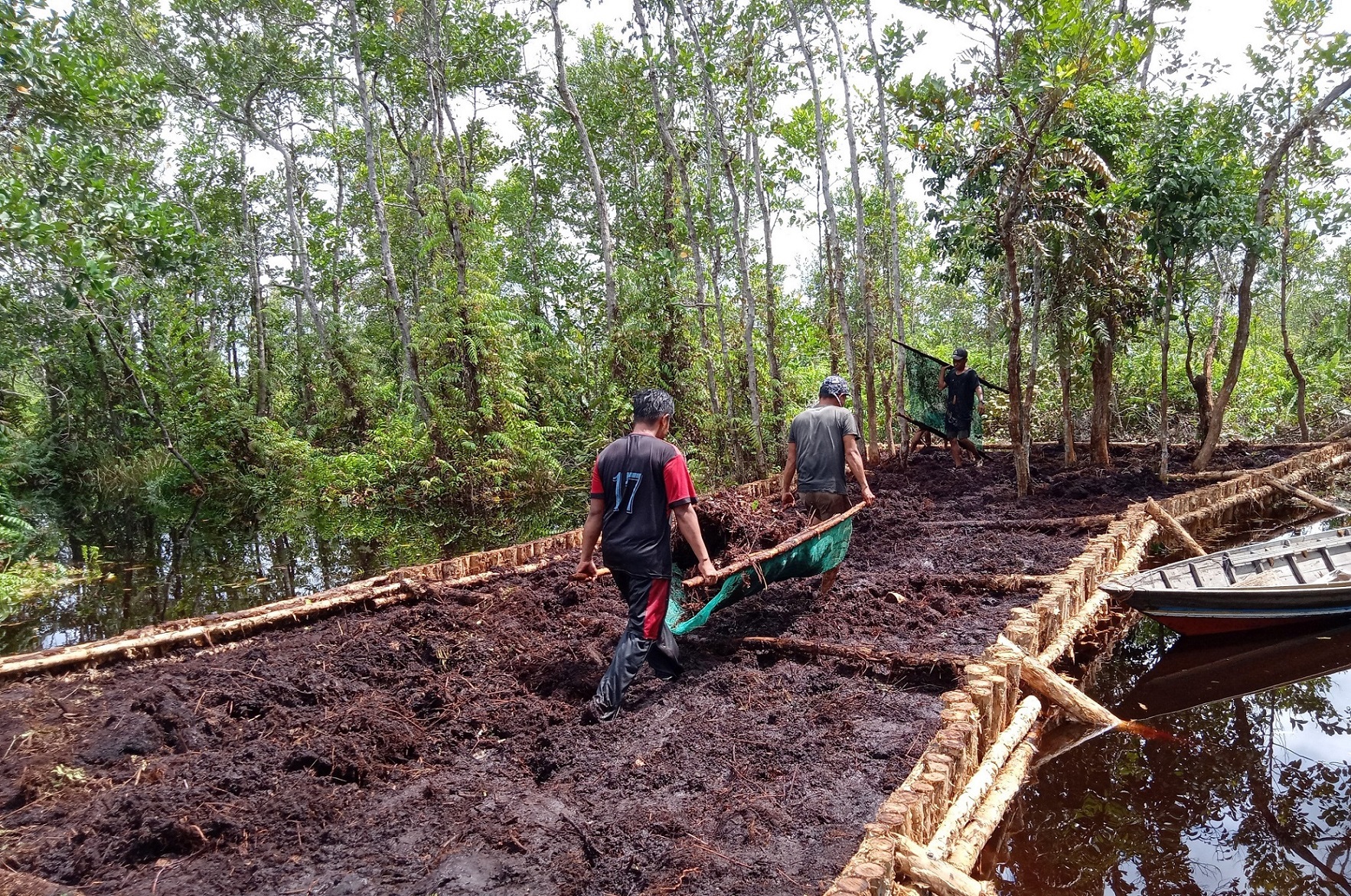

Rehabilitation of peat land forest: Filling the dam with earth.
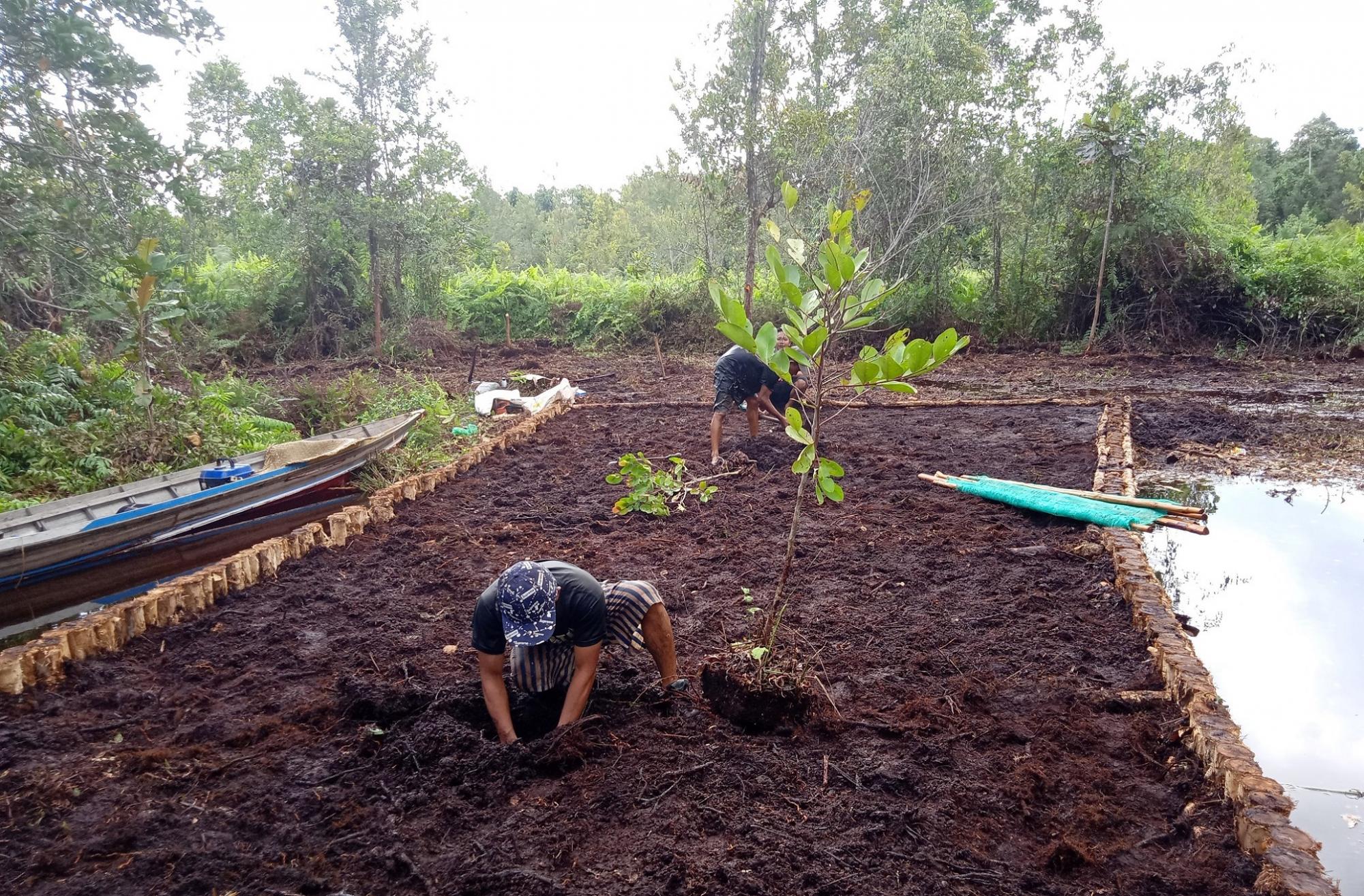

Rehabilitiation of peat land forest: Planting a tree on the dam.
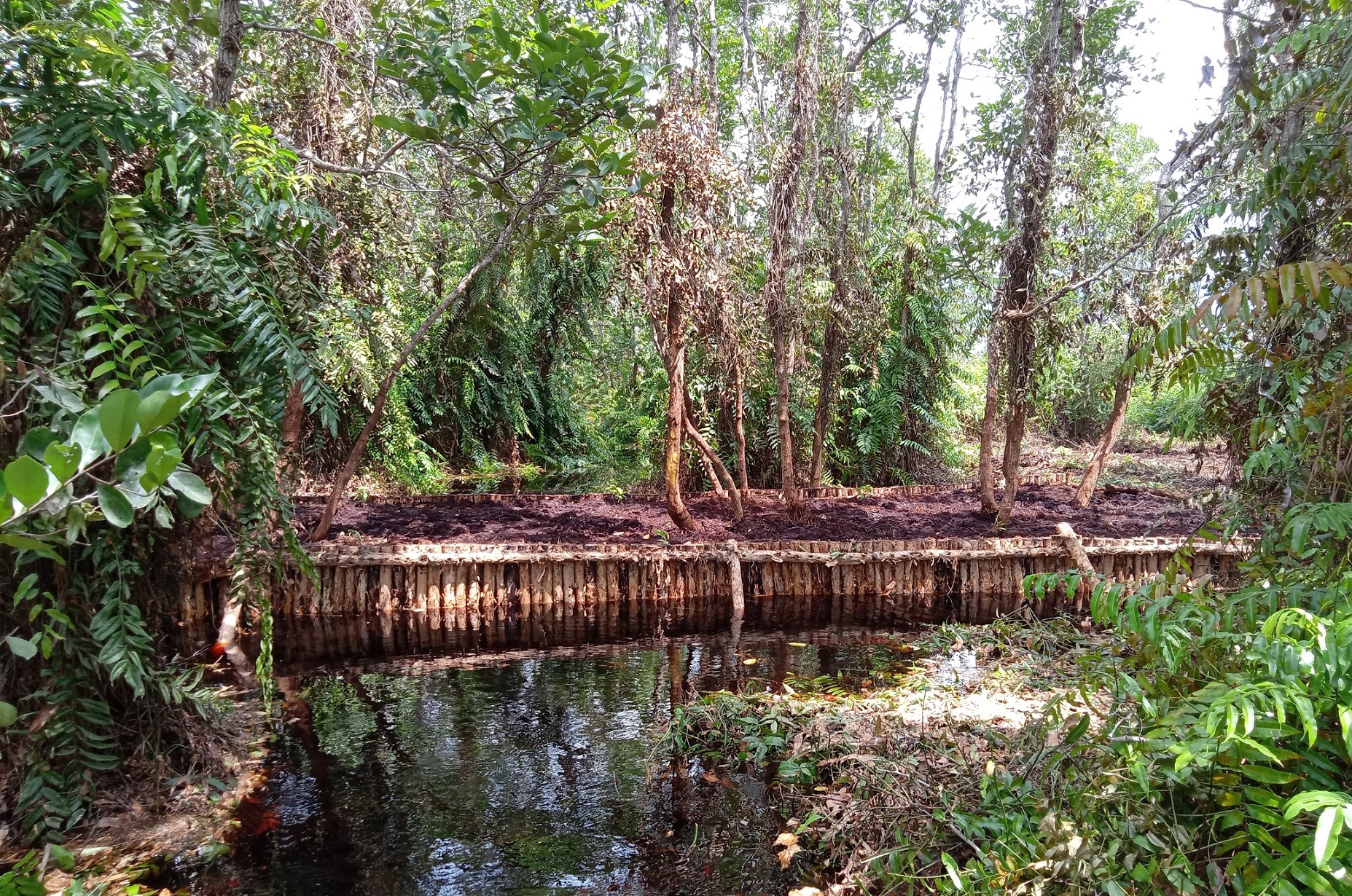

Rehabilitation of peat land forest: Dam with older trees.
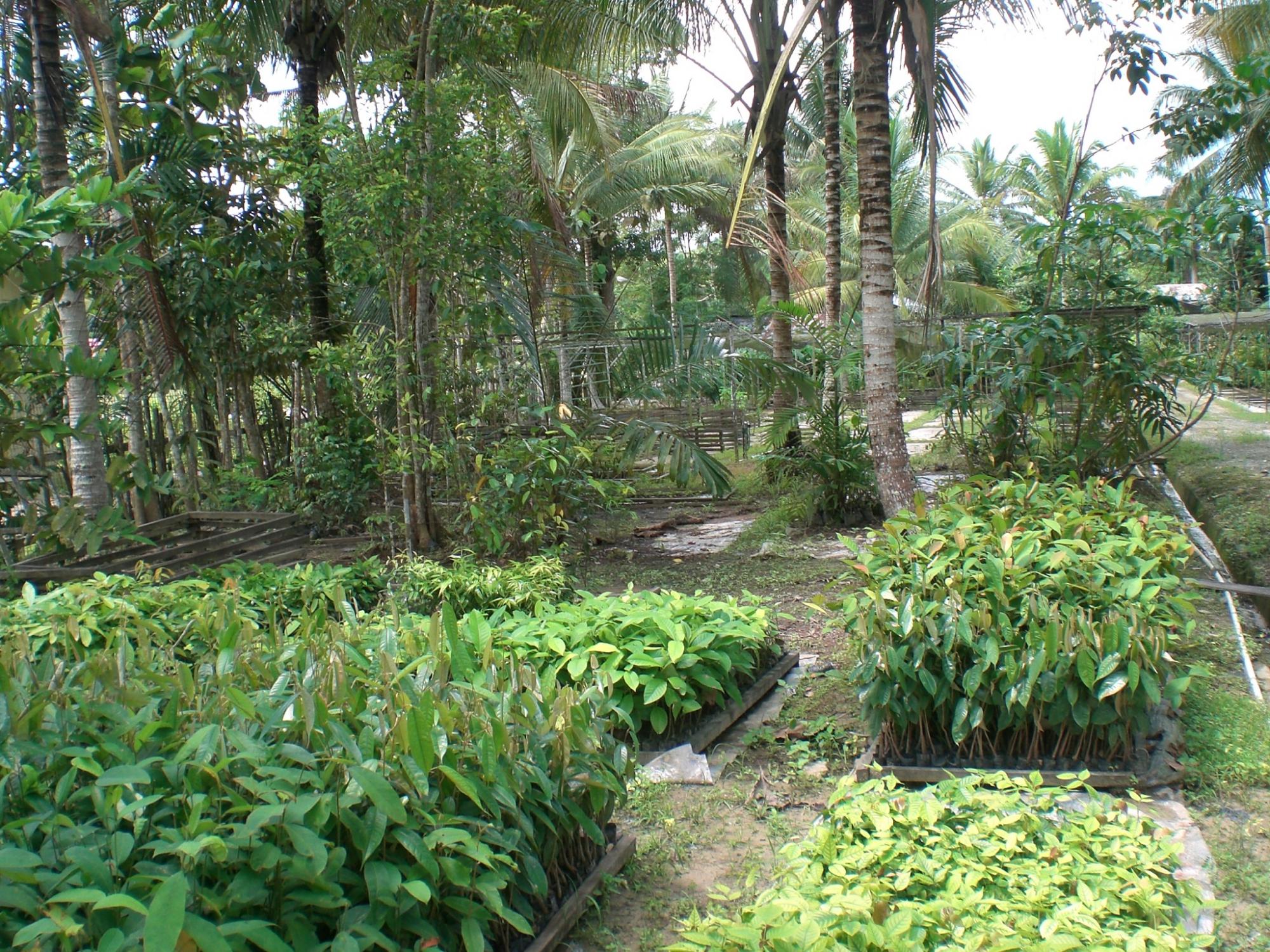

Rehabilitation of peat land forest: View of nursery.
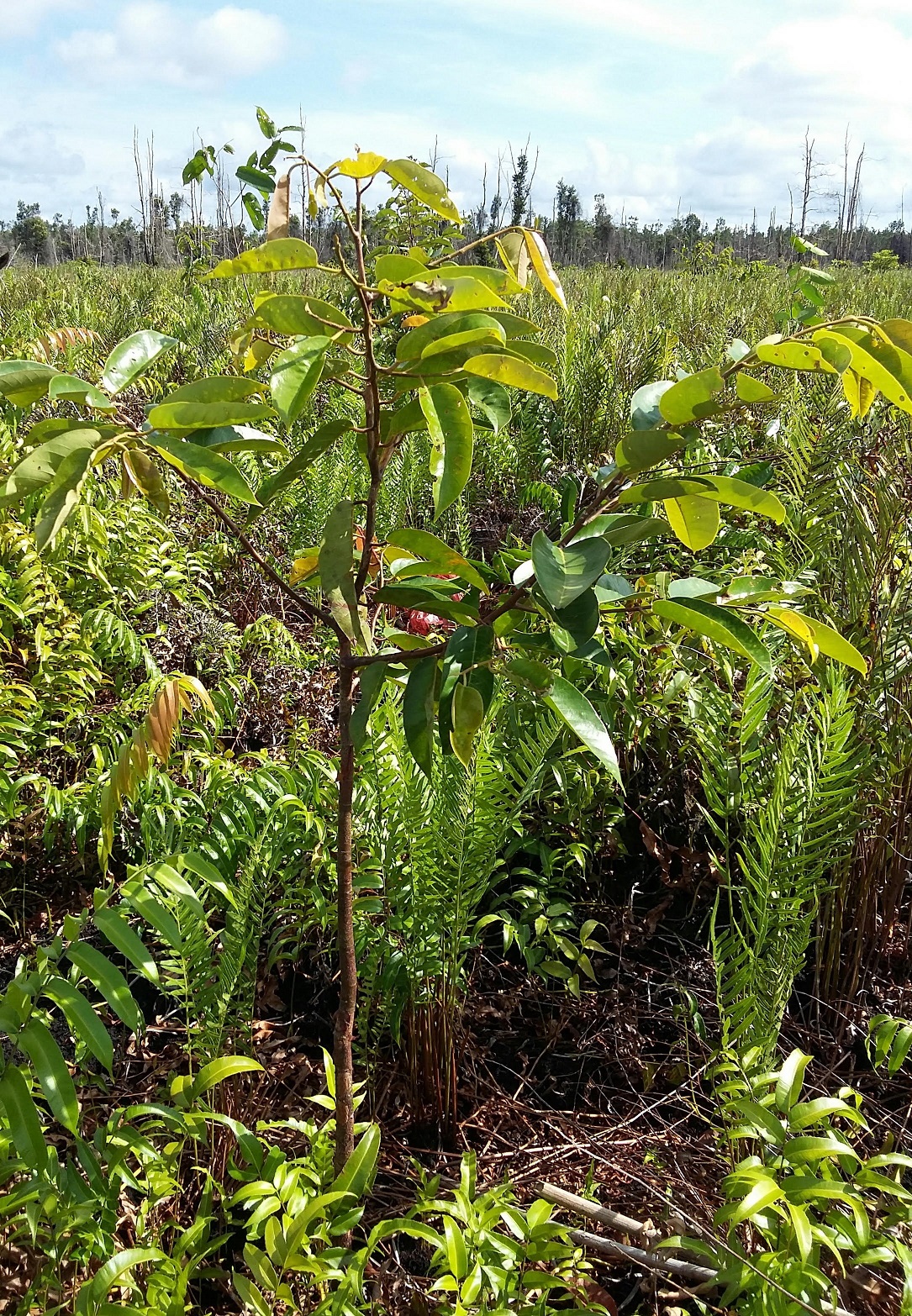

Rehabilitation of peat land forest: Seedling after planting.
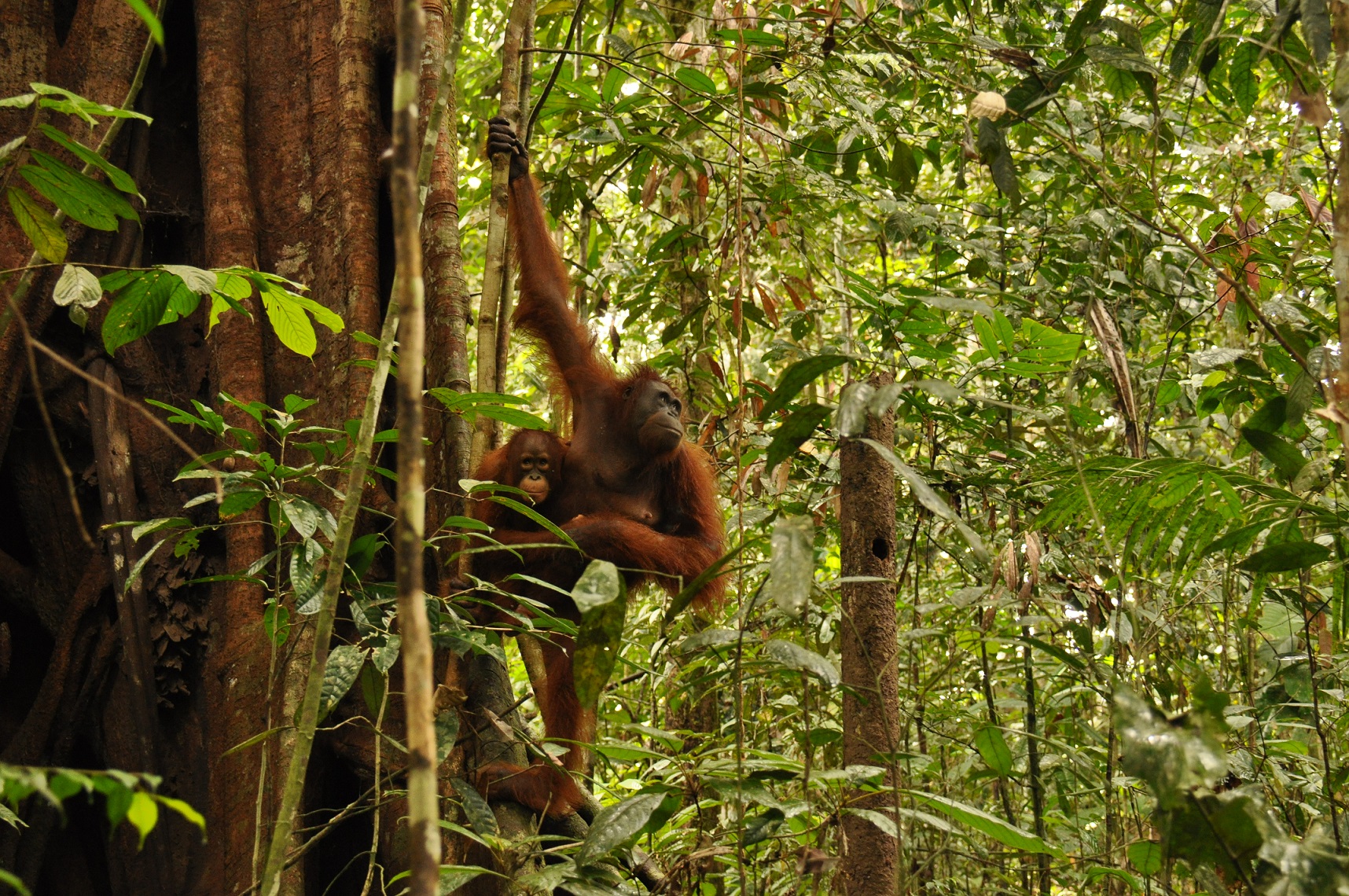

Rehabilitation of peat land forest: Orangutang.