Photostory be Elio Guarionex
Mangrove restoration in the Ramsar site Alvarado Lagoon System
Elio Lagunes, Pronatura Veracruz, A.C.
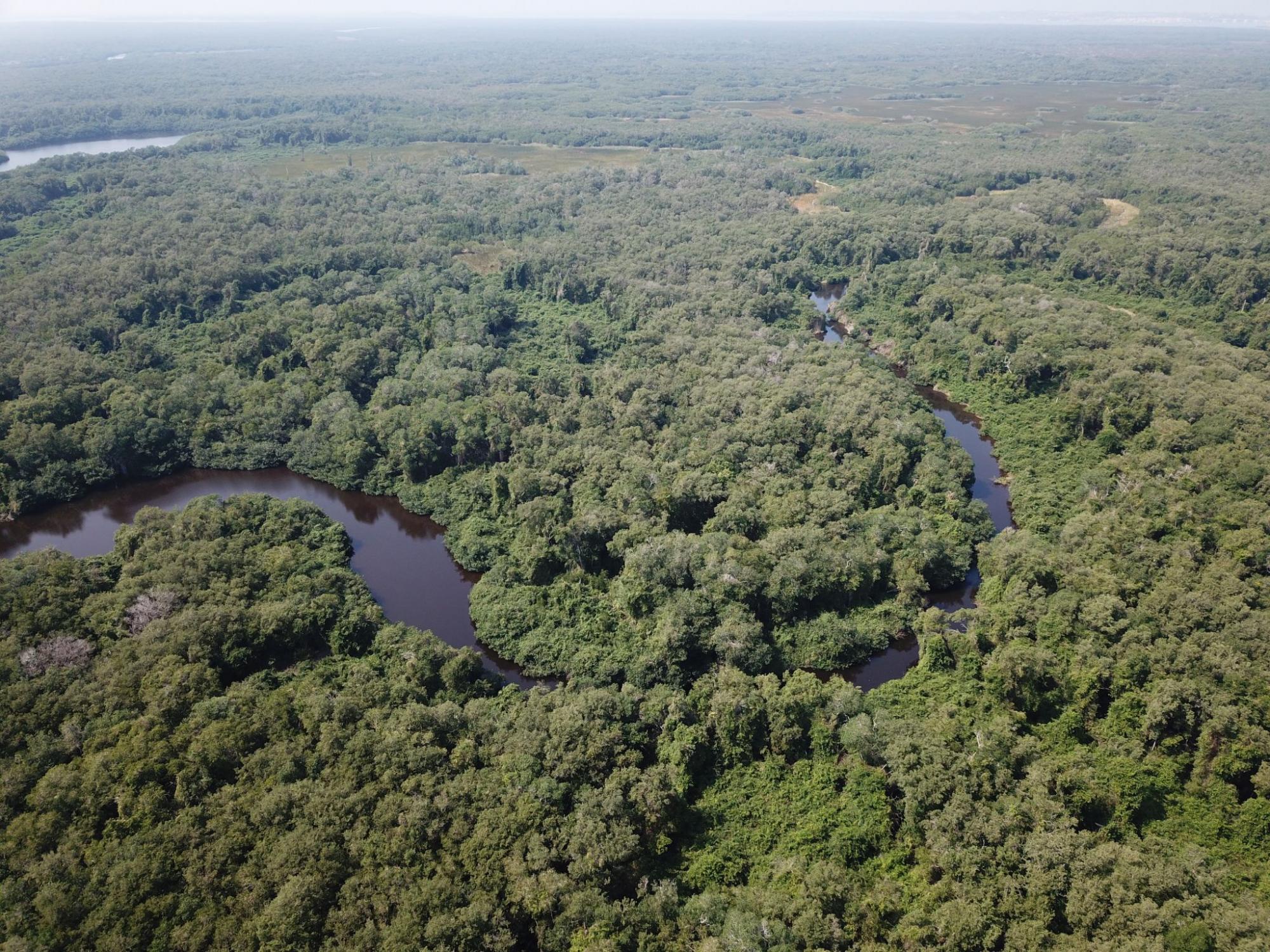
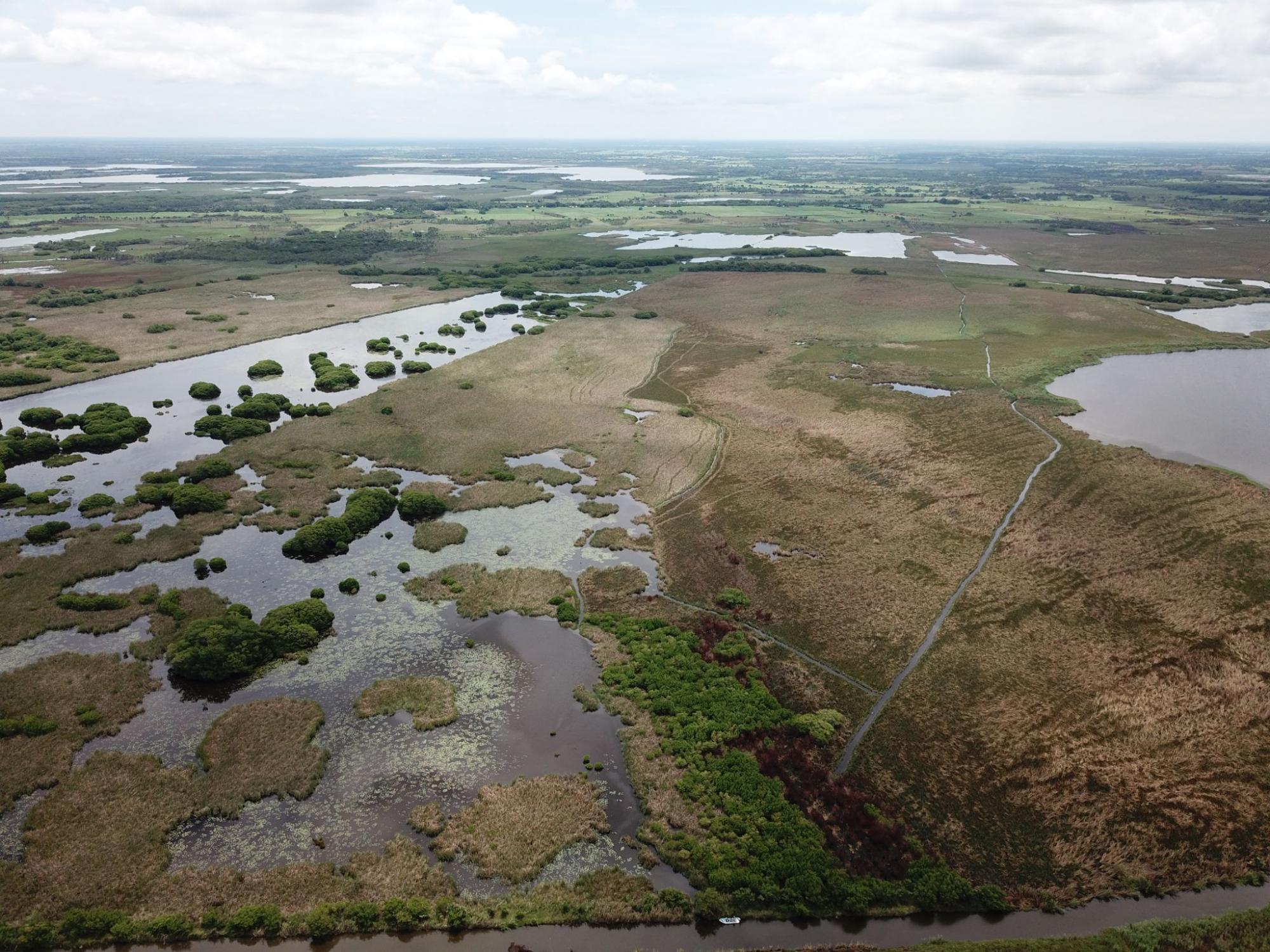
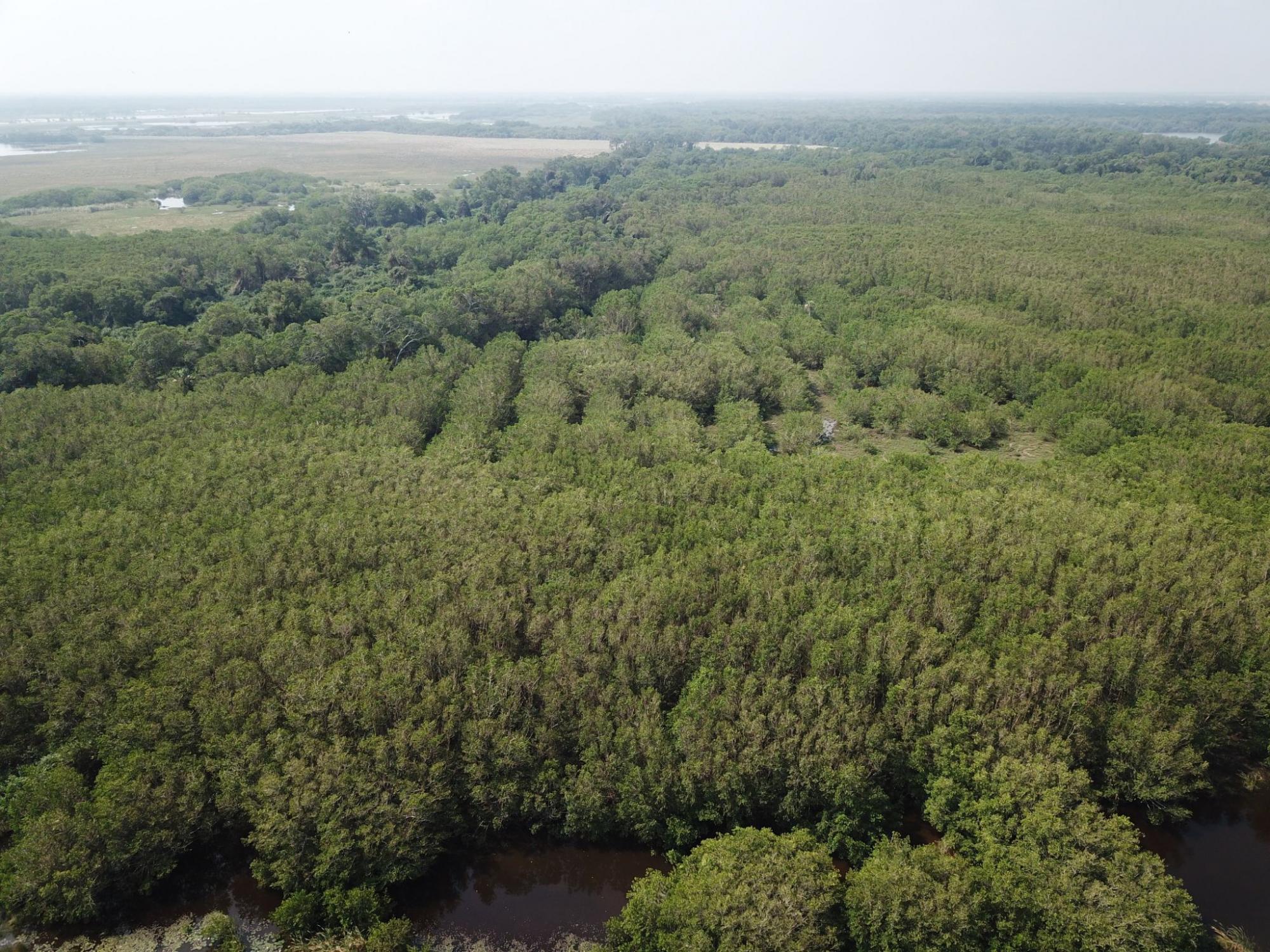
Mangroves live in such saline and anoxic conditions that, where they stand, most other trees cannot even sprout, and their importance as being fish nurseries, storing way more carbon per hectare than most ecosystems and protecting against hurricanes is just a humble part of many things not discovered or understood yet from them. (Picture 1: Mangrove landscape with river meadows in the Ramsar Site "Alvarado Lagoon System", in Veracruz, Mexico)
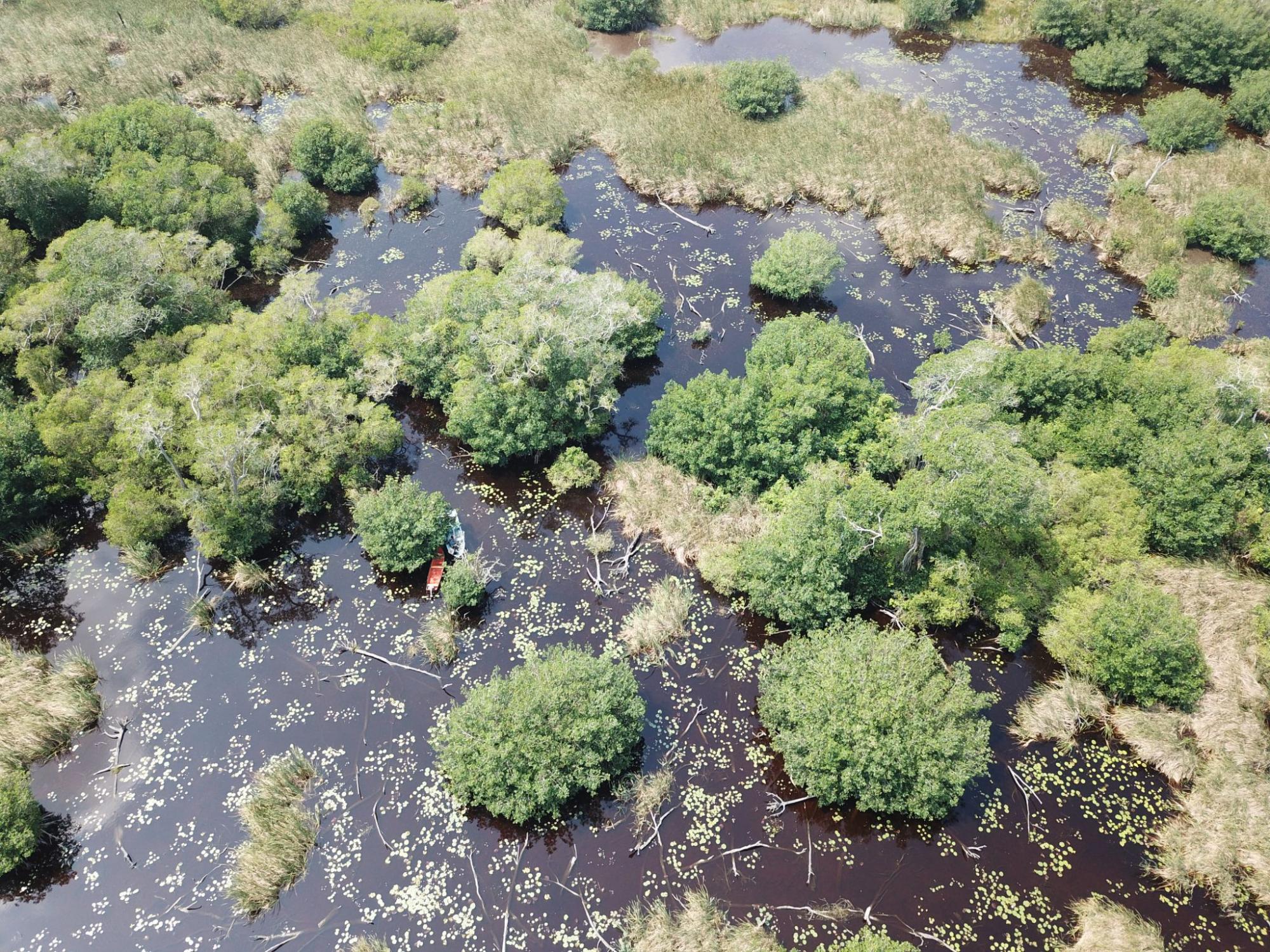
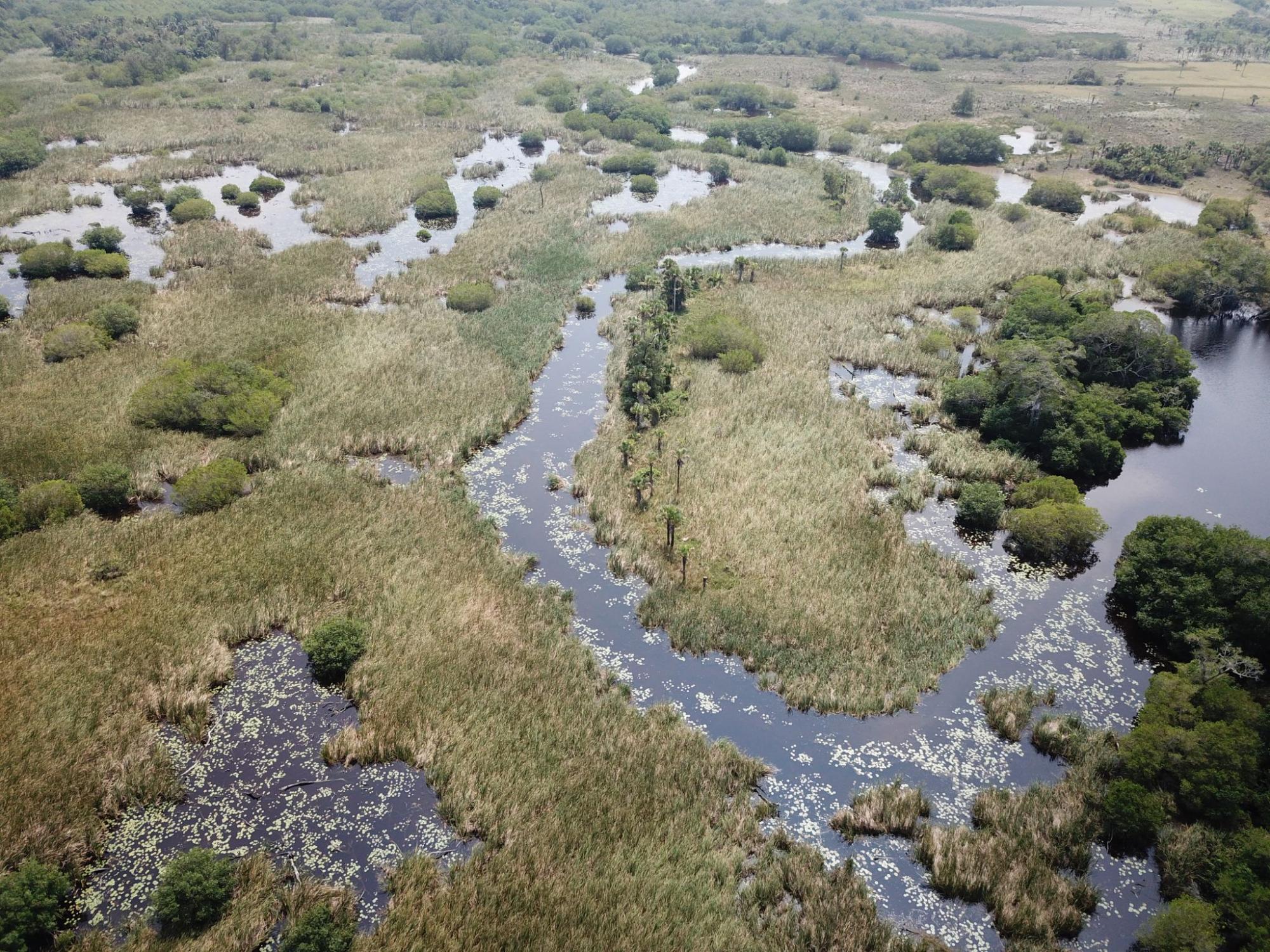
Mangroves are resilient, they recover naturally after most single disturbances but, in many cases the recovery process is hindered by changes in hydrology following hurricanes, by periodical fires or by colonization by other plant species, such as cattail, which is also a natural part of wetland landscapes where mangroves occurr. As it happens with most ecosystems, people are the primary threat to these ecosystem. All along the Gulf of Mexico, wetlands in general have been converted to pasture lands, sugar fields or cleared to build oil rigs. (Pictures: 2, mangrove trunks floating on the water after a disturbance; 3, cattail growing on a former mangrove)
Mangrove restoration has short history in the Alvarado Lagoon System, as well as in Mexico in general, about three decades long, and many things have yet to be learnt about its nature in the region. Pronatura Veracruz, together with the people living next to them, researchers, other NGO's, and local governments as main actors, through a process of trial and error, some valuable lessons have been learnt to ecologically design succesful restorations.
To ensure success, hydrology must be restored or enhanced as a part of the overall restoration effort; channel dredging involves many people, who also see a direct benefit by the increased connectivity between fishing spots. In many cases hydrological restoration alone can bring a mangrove forest back to life, without the need for planting. (Picture 4, local people opening a channel)
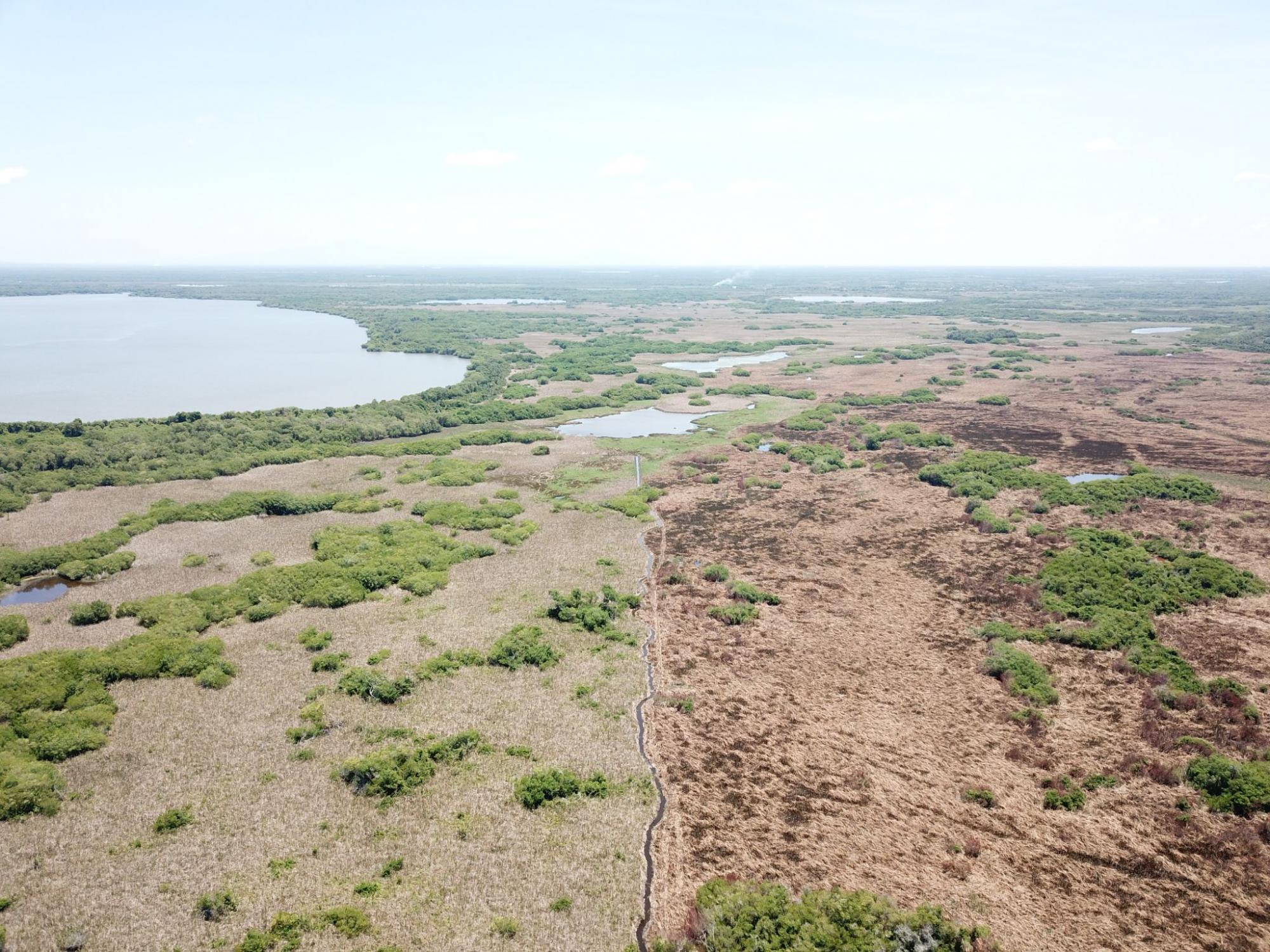
Even though soil is flooded through most of the year, fire is a primary threat to restoration: in the Alvarado Lagoon System, as well as in many other mangroves in Mexico, poachers burn down cattail marshes to frighten turtles and concentrate them in the borders of burnt areas; cattail marshes are also burnt to allow movement of cattle. These fires, most of the time, do not present a major threat to tall, adult mangroves, but bring havoc to young plants in restoration nucleii. In places were arson occurrs, firebreaks are primordial as a part of the restoration. Through employing people in restoration, we hope to give people other means of life and we expect to see a reduction this kind of poaching (Pictures: 5, wildfire arson; 6, fire marks; 7, a firebreak that kept fire out of a site which will undergo restoration)
Floods can also drown small mangrove plants, when the water level surpasses their height; in the past, many ground-level restorations were lost to floods. To ensure that mangroves can thrive during the flood months, little mounds or stands of silt and cattail stems are made to host mangrove nucleii, resembling the "chinampas", an ancient aztec technique used to grow orchards on the lake of Texcoco. (Pictures: 8, pathways of restoration nucleii on cattail growing on an area which was once mangrove; 9, five year old restoration site, using nucleation techniques; 10; 10 year old restoration site, using nucleation techniques)
References:
Lewis, Roy R., (2005). Ecological engineering for successful management and restoration of mangrove forests. Ecological Engineering, 24, 4. P. 403-418.

Mangrove landscape in Alvarado.

Mangrove stands after disturbance.

Cattail on former mangroves.
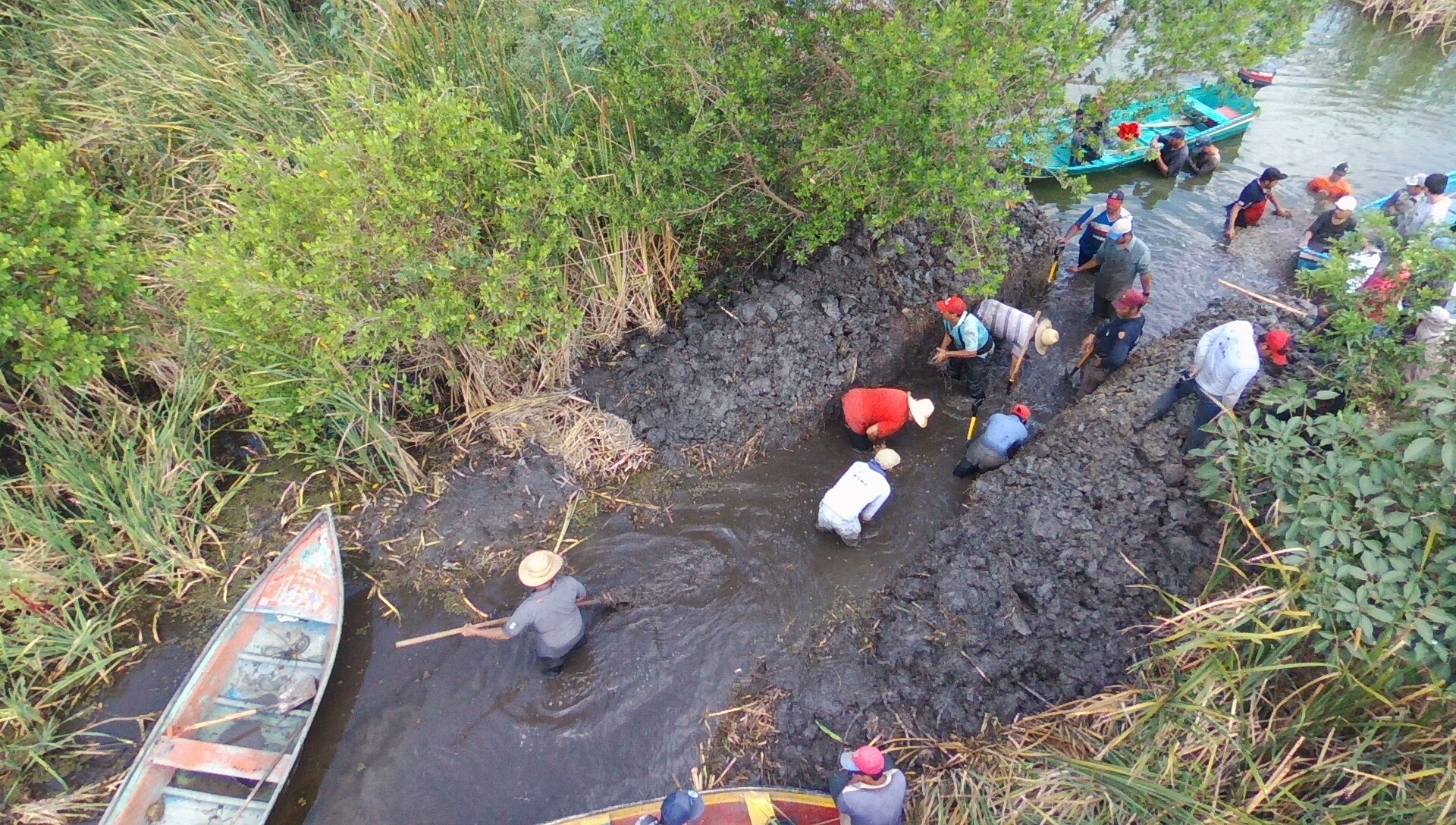

Opening a channel.
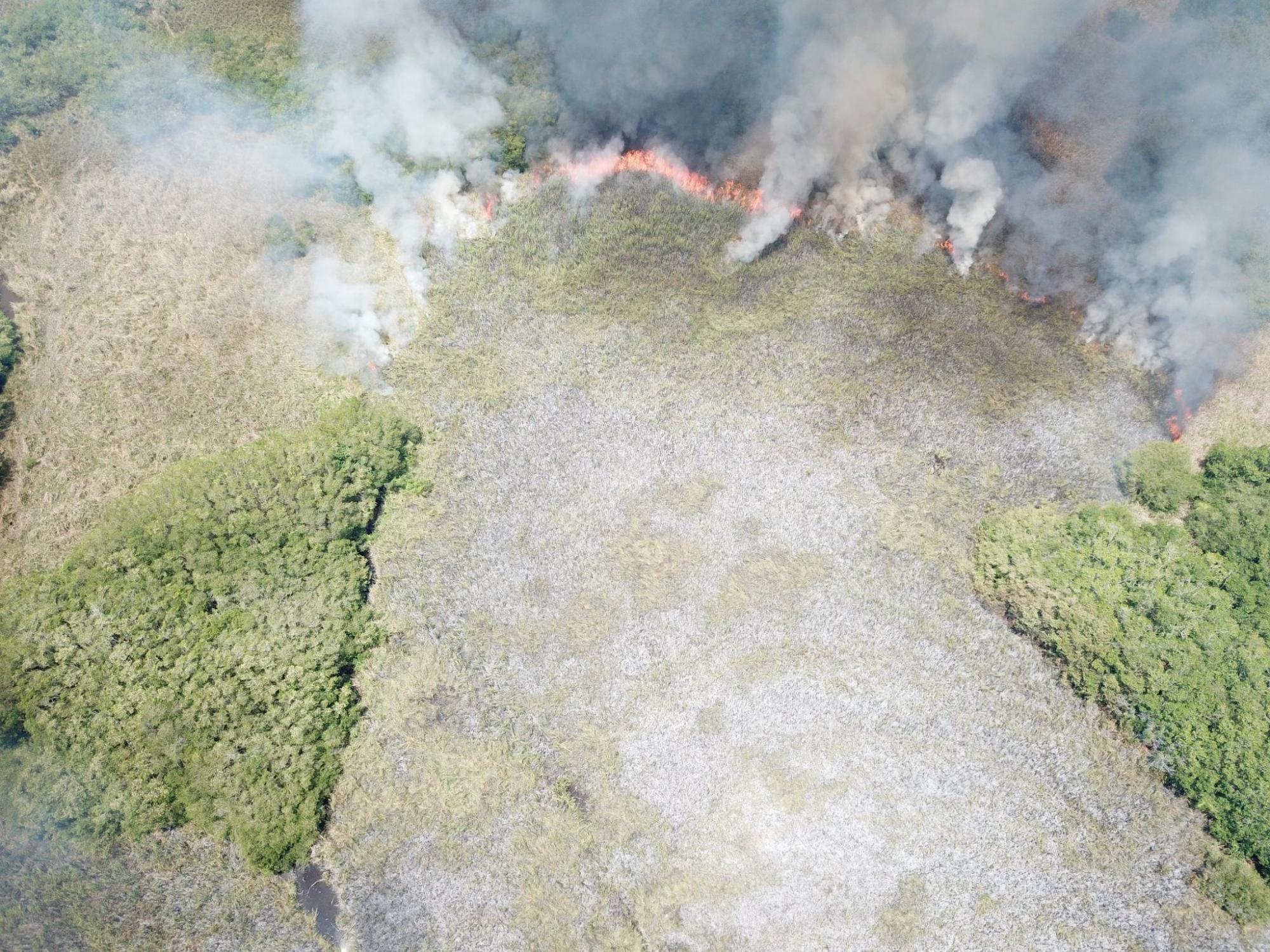

Arson.

Fire marks on restored area.

Firebreak.
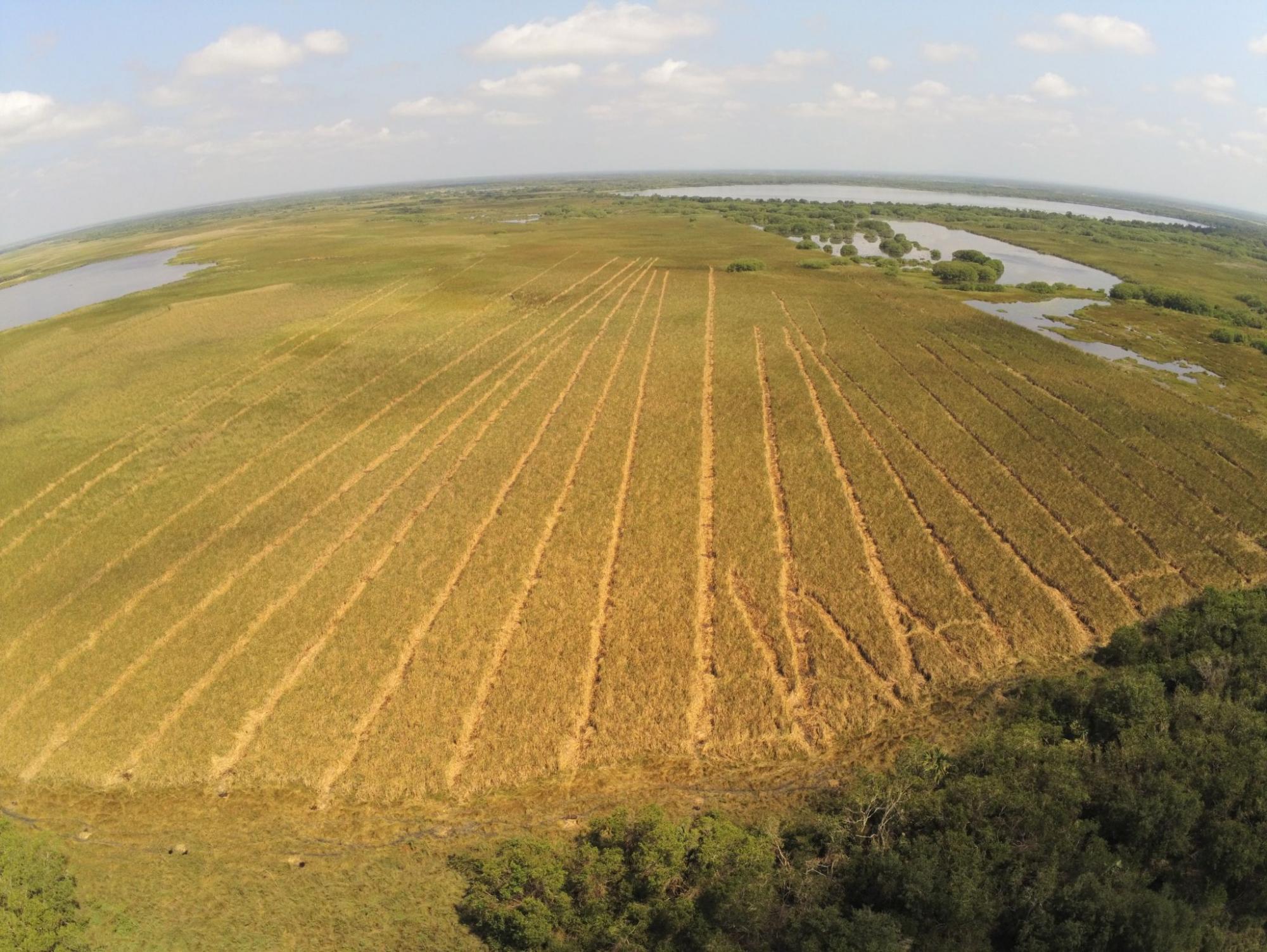

Nucleation Pathway.
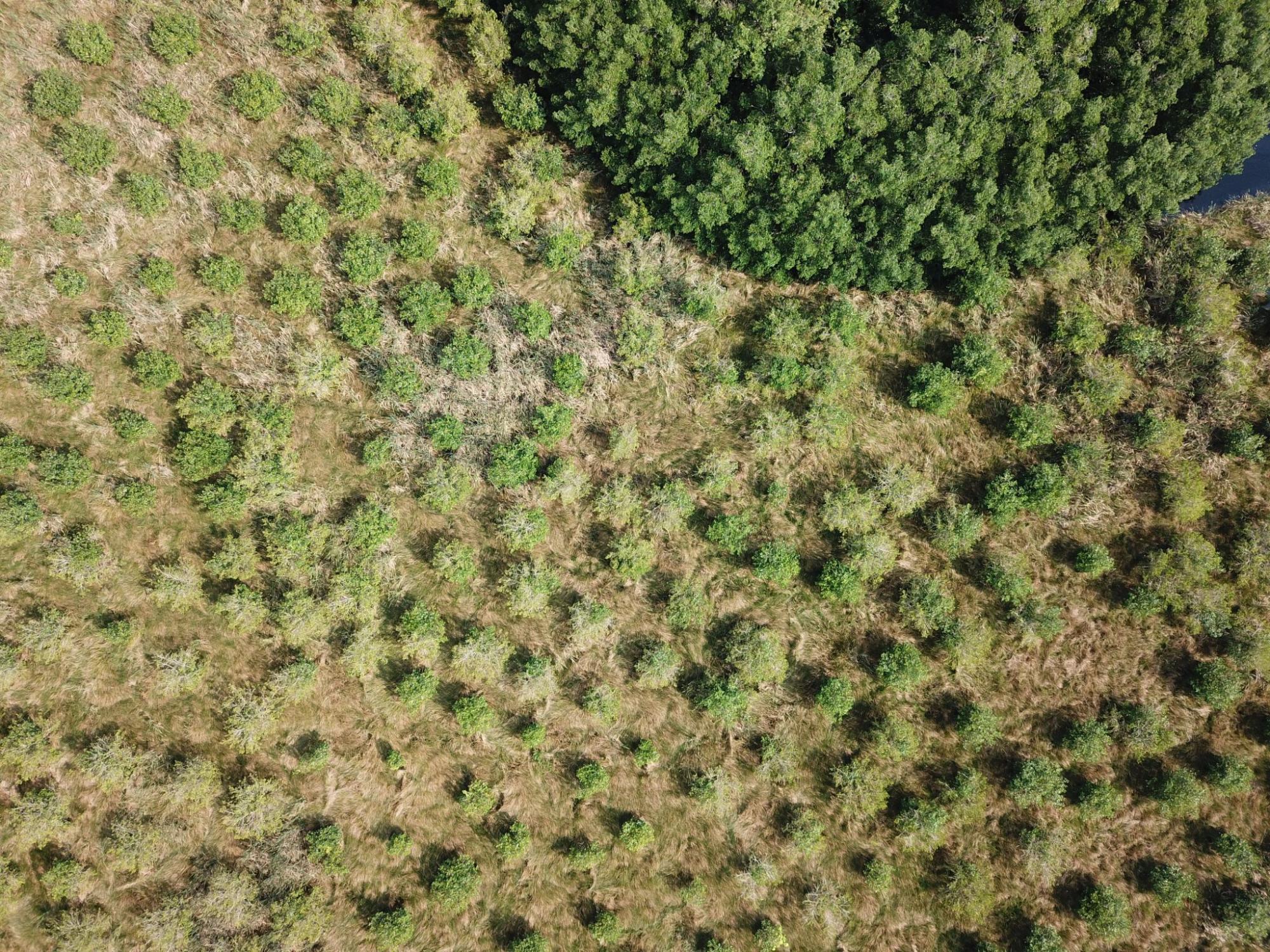

Five years old restoration.

Ten year old restoration.